Research
Overview
The overarching aim of the Train2Target programme was to deliver leads for a new generation of innovative antibacterials to treat infections by multi-drug resistant pathogens. This has been achieved by exploiting the mechanisms that govern the growth of the outer membrane (OM) and a thin peptidoglycan (PG) layers and their coordination to highlight novel targets for antimicrobial discovery.
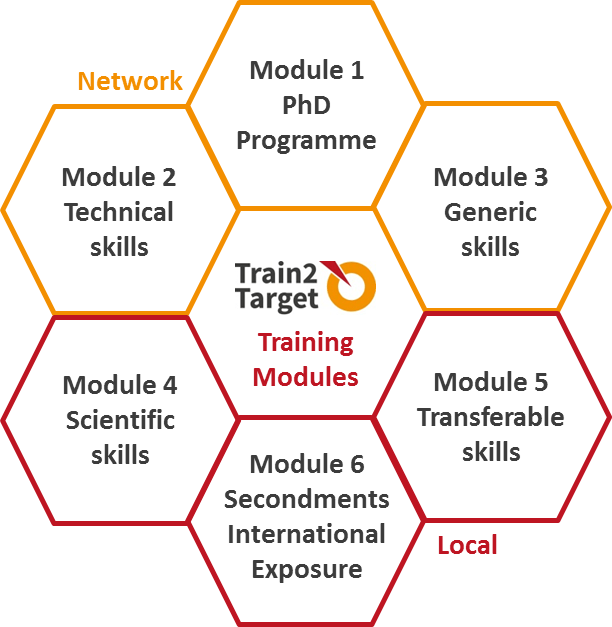
More particularly, the Train2Target network has been training over the last 4 years 15 Early Stage Researchers (ESRs) in all scientific and non-scientific aspects related to the drug discovery process, including the following:
- Dissecting at the molecular level the function of the core envelope machineries
- Investigating how the activities of envelope machineries are orchestrated and coordinated with PG synthetic machineries elongasome and divisome to ensure appropriate growth of the envelope layers during the cell cycle
- Developing innovative screening strategies/ technologies to identify molecules inhibiting envelope biogenesis
Key Facts
Programme:
H2020-MSCA-ITN-2016 (ETN)
Duration:
01.01.2016-31.12.2020
Budget:
3.6 million euro
Factsheet:
Workplan
The T2T research programme is based on 3 scientific work packages (WPs) and 3 WPs dedicated to the training, the dissemination and management of the research results. Each of our 15 ESRs will focus on the research within one of these WPs while getting an insight into the other WPs as part of the network-wide scientific training workshops.
The University groups and the industry partners will contribute equally to the development of the research plan and to its excellence.
WP1
Molecular dissection of protein machineries that orchestrate envelope growth aimed to dissect at the molecular level the function of the Lpt and BAM envelope machineries by using interdisciplinary approaches based on an array of genetic, biochemical, biophysical and structural biology techniques. The assembly of Lpt and BAM machineries and the interaction with their substrates (LPS and OMPs, respectively) was crucial for their function and was an excellent target for inhibition.
WP2
Cross-talk between core envelope machineries during cell cycle addressed the coordination of envelope machineries. We explored how the Lpt and BAM machineries monitored the activities of the PG synthetic machineries (elongasome and divisome) to drive appropriate growth of the envelope layers.
WP3
Publications
List all the project publications in the Fold-out-section below.
- Laguri, C. ; Sperandeo, P. ; Pounot, K. ; Ayala, I. ; Silipo, A. ; Bougault, C.M. ; Molinaro, A. ; Polissi, A. ; Simorre, J.P. (2017). Interaction of lipopolysaccharides at intermolecular sites of the periplasmic Lpt transport assembly. Scientific Reports, 7, 9715-1-9715–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10136-0.
- Laguri, C., Silipo, A., Martorana, A.M., Schanda, P., Marchetti, R., Polissi, A., Molinaro, A., Simorre, J.P. (2018) Solid State NMR Studies of Intact Lipopolysaccharide Endotoxin. ACS Chemical Biology 2018 13 (8), 2106-2113 DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.8b00271.
- Sperandeo, P.; Martorana, A.M.; Polissi, A. (2017). The lipopolysaccharide transport (Lpt) machinery : A nonconventional transporter for lipopolysaccharide assembly at the outer membrane of Gram-negative
bacteria. J Biol Chem https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R117.802512. - Meiresonne, N. Y., Consoli, E., Mertens, L. M. Y., Chertkova, A., Goedhart, J., & den Blaauwen, T. (2018). Superfolder mTurquoise2ox optimized for the bacterial periplasm allows high efficiency in vivo FRET of cell division antibiotic targets. BioRxiv, 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1101/415174.
- Peters K, Pazos M, Edoo Z, Hugonnet JE, Martorana A, Polissi A, VanNieuwenhze MS, Arthur M, Vollmer W. 2018. Copper inhibits peptidoglycan LD-transpeptidases suppressing b-lactam resistance due to by-pass of Penicillin-binding proteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 115, 10786-10791.
- Morè N, Martorana AM, Biboy J, Otten C, Winkle M, Gurnani Serrano CK, Monton Silva A, Atkinson L, Yau H, Breukink E, den Blaauwen T, Vollmer W and Polissi A. (2018) Peptidoglycan remodelling enables E. coli to survive severe outer membrane defect. mBio (in press).
- Cleverley R, Ruttner Z, Rismondo J, Corona F, Tsui, HCT, Alatawi F, Daniel R, Haldebel S, Massidda O, Winkler M, Lewis R, (2019). The cell cycle regulator GpsB functions as cytosolic adaptor for multiple cell wall enzymes, Nat Commun 10, 261. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-08056-2.
7th World Congress and Exhibition on Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance, London, UK from 16-17 March 2020.
Gordon Research Conference: New Antibacterial Discovery and Development, Lucca, Italy from 1-6 March 2020.
Great Wall Symposium 2019, Paris, France from 25-27 September 2019.
FEMS 2019 – 8th Congress of European Microbiologists, Glasgow, Scotland from 7-12 July 2019.
EMBO Workshop – Bacterial cell division: Closing the gap, Lund, Sweden from 9-12 June 2019.
ESCMID/ASM Conference on Drug Development – to Meet the Challenge of Antimicrobial Resistance, Lisbon, Portugal, from 4-7 September 2018.
Gordon Research Conference (GRC) Bacterial Cell Surfaces, West Dover, Vermont, US from 24-28 June 2018.
Practical Aspects of Small Molecule Drug Discovery 2018, Wellcome Genome Campus, Hinxton, Cambridge, UK,
from 17-22 June 2018.
Challenges and new concepts in antibiotic research, Institut Pasteur, Paris from 19-21 March 2018.
Great Wall symposium 2017, São Rafael, Algarve, Portugal, from 24-27 September 2017.
FEMS 2017 – 7th Congress of European Microbiologists, Valencia, Spain from 9-13 July 2017.
Science slams
In case you have been wondering what each ESR has been researching within the Train2Target project they have created short videos to introduce their area of research. These videos have been created as part of the Train2Target Science Slams which aim to provide an educational resource to the general public and other interested audiences.
Project overview
ESR2 & ESR10
Drug discovery
ESR12
LPT Machinery
ESR1, ESR6 & ESR11
Introducing BAM
ESR7 & ESR9
Rcs system in Escherichia coli
ESR4 & ESR5
What are antibiotics?
ESR15
Peptidoglycan
ESR8 & ESR14
Drug discovery
ESR3

